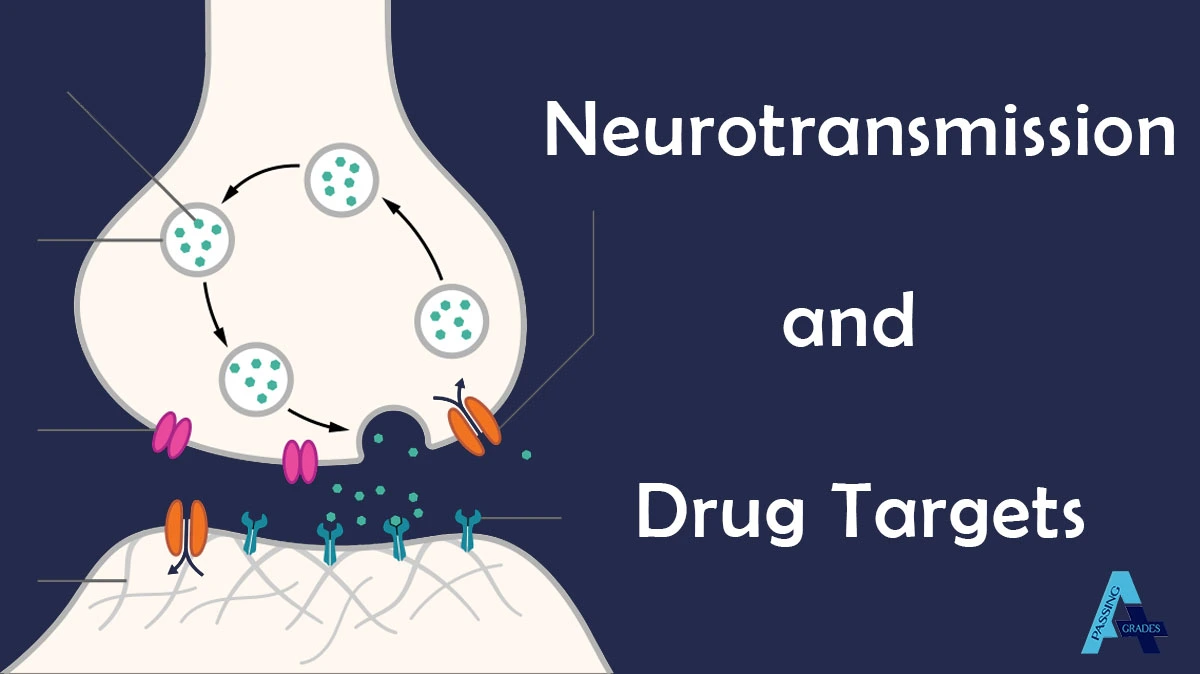
Understanding how neurons communicate and how drugs influence this process is central to neuroscience and pharmacology. Below, we break it down into simple questions and answers to make complex concepts more approachable.
Agonists and Antagonists
Q: When a full agonist is absent, a partial agonist acts as a…
A: Net agonist
Q: In the presence of a full antagonist, a partial agonist acts as a…
A: Net antagonist
Neurons and Their Structures
Q: What are dendrites?
A: Tree-like branches that extend from the cell body. They form chemical communication with axons, the soma, and other dendrites. They also contain dendritic spines.
Q: What is the soma?
A: The cell body that contains organelles such as mitochondria, ER, synaptic vesicles, and mRNA.
Q: What is the axon?
A: A tail-like structure extending from the cell body, responsible for electrical and chemical neurotransmission.
Q: What is a synapse?
A: The site of chemical transmission between neurons.
Q: What is presynaptic transmission?
A: Anterograde chemical transmission (from presynaptic to postsynaptic).
Q: What is postsynaptic transmission?
A: Retrograde chemical transmission (from postsynaptic to presynaptic).
Q: What is the synaptic cleft?
A: The gap where chemical transmission occurs between neurons.
Q: What are the main types of chemical communication between neurons?
- Axodendritic: Axon → dendrite
- Axosomatic: Axon → cell body
- Axoaxonic: Axon → axon
For more questions focused on chemical transmission and neurotransmitter interactions, try this free Chemical Neurotransmission Practice Set with Test Bank.
Communication between Neurons
Q: What is electrical communication?
A: Communication within a neuron.
Q: What is chemical communication?
A: Communication between neurons.
Q: What is excitation-secretion coupling?
A: The process where electrical impulses in a presynaptic neuron are converted into a chemical signal at the synapse, causing neurotransmitter release.
Q: What is classic synaptic neurotransmission?
A: Electrical stimulation of a presynaptic neuron triggers chemical messengers that stimulate postsynaptic receptors.
Q: What is retrograde neurotransmission?
A: Communication from the postsynaptic neuron back to the presynaptic neuron.
Q: What are examples of retrograde neurotransmitters?
A: Endocannabinoids, nitric oxide, and neurotrophic factors.
Q: What is volume neurotransmission?
A: Transmission without a synapse. Neurotransmitters diffuse to distant neurons, e.g., dopamine in the prefrontal cortex.
Q: What are monoamine autoreceptors?
A: Receptors located on dendrites and soma that inhibit impulse flow when bound by monoamines released from the same neuron.
Neurotransmitters Practice Set
Q: What are the main neurotransmitters?
- Serotonin (SSRIs)
- Norepinephrine (NRIs)
- Dopamine (D2 antagonists) – important in psychosis treatment
- Acetylcholine – memory and parasympathetic functions
- Glutamate – excitatory neurotransmitter
- GABA – inhibitory neurotransmitter
Q: What are endogenous substrates?
A: Neurotransmitters produced naturally by the body.
- Examples: β-endorphin (morphine-like), anandamide (marijuana-like), adrenaline
Q: What are exogenous substrates?
A: Neurotransmitters or drugs introduced into the body that mimic natural neurotransmitters.
- Examples: Antidepressants, anxiolytics, hallucinogens
Signal Processing in the Brain
Q: What is signal transduction?
A: The cascade of events after postsynaptic receptor stimulation.
Q: What is gene expression in this context?
A: The ultimate function of neurotransmission—determining protein production.
Q: What is epigenetics?
A: The system that turns genes on or off by modifying chromatin structure in the nucleus.
Q: What contributes to mental disorders?
A: Abnormal gene expression due to inherited mutations that impair neuron function.
Drug Targets in Neurotransmission
Q: Approximately how many drugs target neurotransmitters?
A: About one-third of all drugs in clinical practice.
Q: How many target receptors and G-proteins?
A: Another one-third.
Q: How many target enzymes?
A: About 10 percent.
Q: Do any target ion channels?
A: Yes, but only a small proportion.
Q: What are the main targets of drug action?
- Neurotransmitters
- Transporters
- Receptors
- Enzymes
- Ion channels
Q: What are the molecular targets of psychotropic drugs?
- 12-transmembrane-region transporter
- 7-transmembrane-region transporter
- Enzyme
- 4-transmembrane-region ligand-gated ion channel
- 6-transmembrane-region voltage-gated ion channel
Neurotransmitter Transporters Exam Prep Set
Q: What are the two main types of neurotransmitter transporters?
A: Presynaptic reuptake transporters and vesicular storage transporters.
Q: What are subclasses of plasma membrane transporters?
- Sodium/chloride coupled transporters (SLC6 gene family): serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine, GABA, glycine
- High-affinity glutamate transporters (SLC1 gene family)
Q: What are intracellular synaptic vesicle transporters?
A: Transporters from the SLC18 and SLC17 gene families that move monoamines and amino acids into vesicles.
Q: What is the role of neurotransmitter transporters?
A: To clear neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft and recycle them for future use.
For more detailed exam-style questions on this topic, explore the Test Bank for Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology (5th Edition).

0
1333